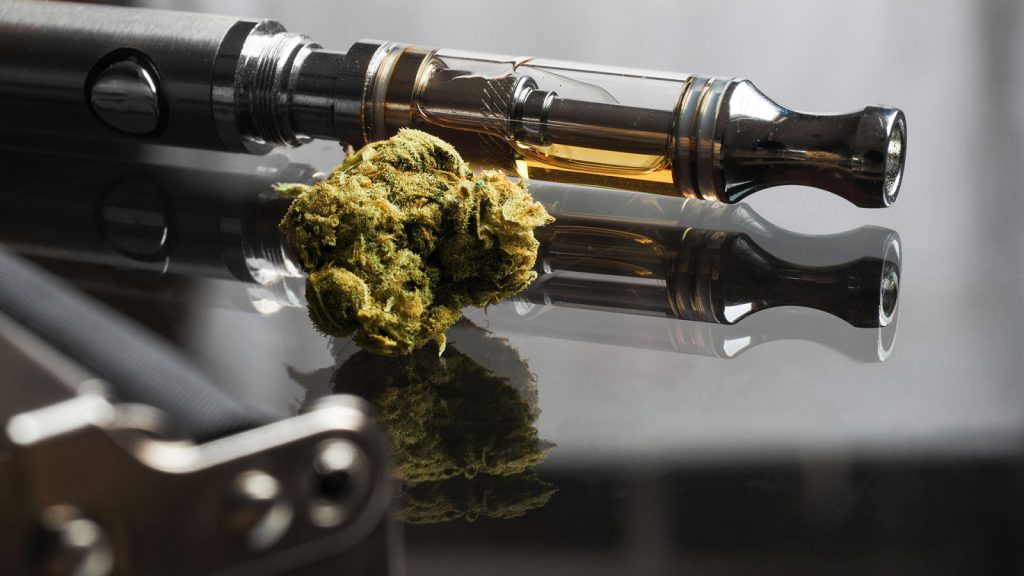
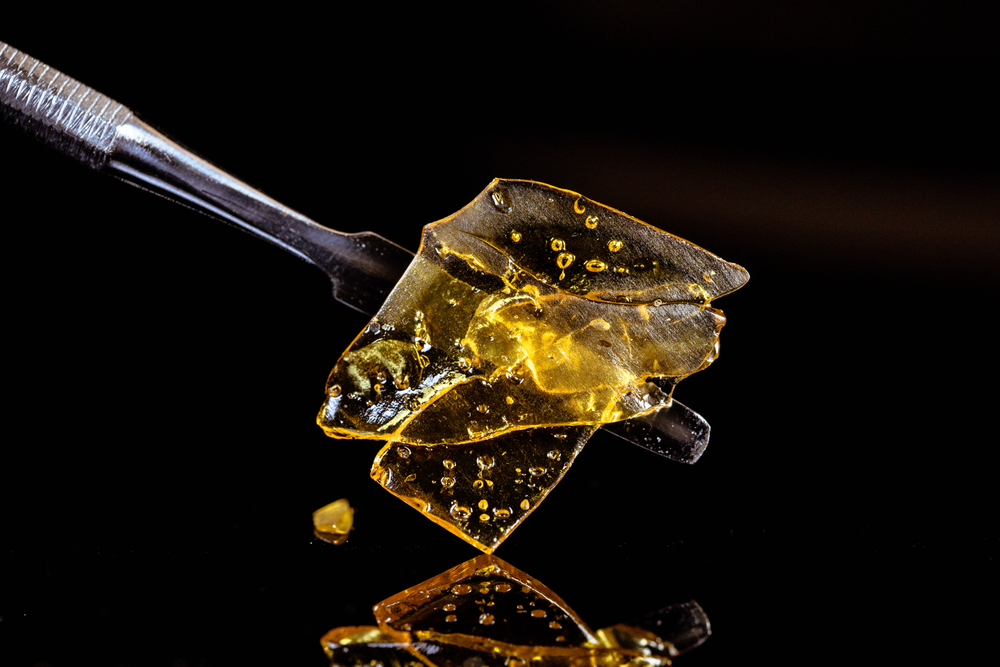
If you take an interest in cannabis culture, I'm betting at least once you've seen that bongs with unusual bowls and beautiful amber-like stuff.
Yep, this is it, today we talk about cannabis concentrates.
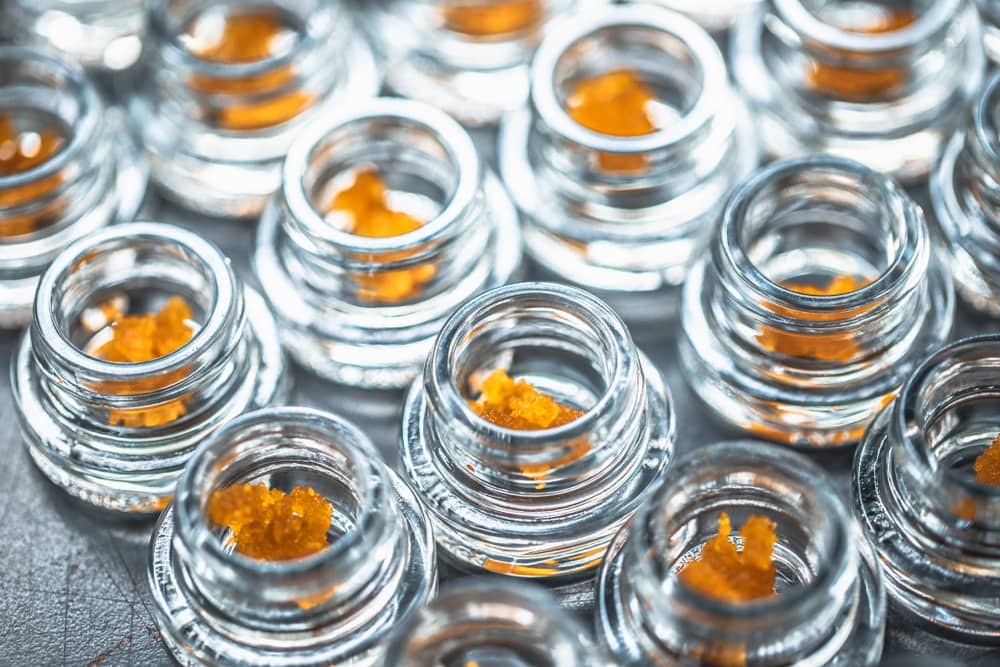

What are cannabis concentrates and extracts?
The cannabis plant contains myriads of chemical structures, but the most interesting for the majority of us psychoactive components contained in small mushroom-shaped structures. These crystalline formations make up part of structures known as trichomes, which may be found on many plants, including cannabis. Cannabis trichomes are primarily protective structures produced by female plants when flowering. Their intense bitter taste and strong aromas render the plant unpalatable to herbivores and, they also inhibit some fungal growth.
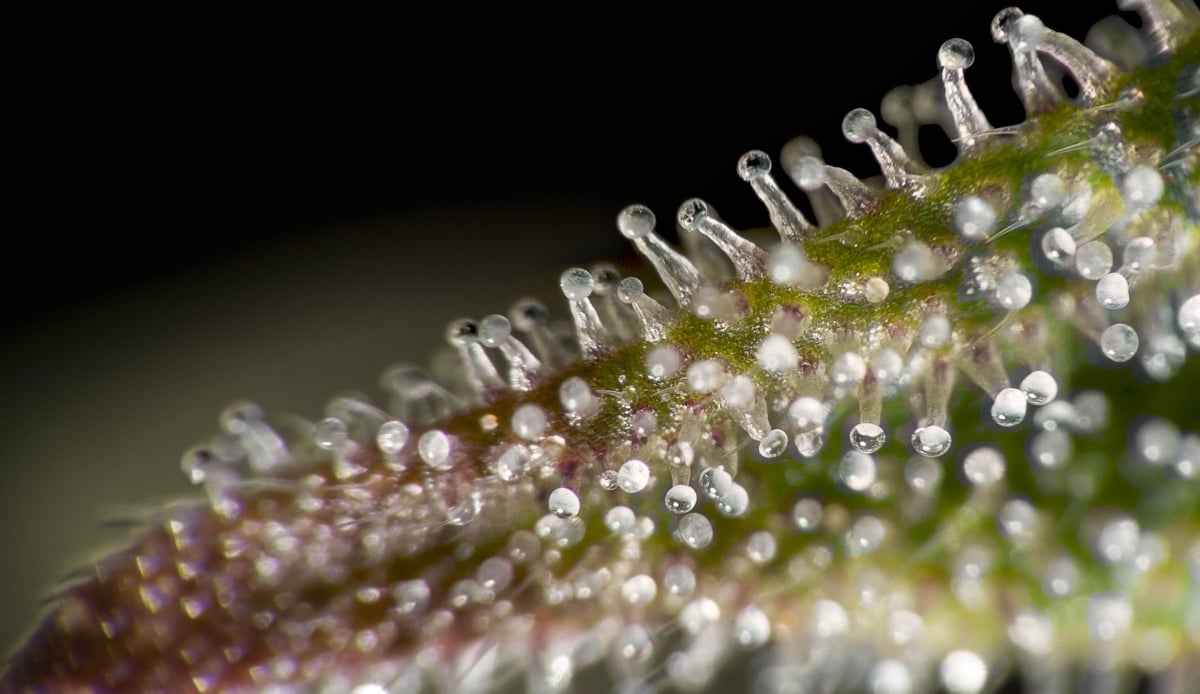

All methods of extraction are different ways to collect trichomes inherently. All types of extracts represent a mass of trichomes, whereas their appearance and consistency depend on purity and method for producing.
Concerning using terms as "extract" and "concentrate", without getting into some exceptions: most products produced using a solvent are called extracts, and what getting with other methods and processes like mechanical actions or water - called concentrates. These definitions came from the scope of medicinal plants and in my personal opinion separate them within the subject of cannabis makes little sense. So, further, we would use the word "extract".
There are quite a lot of extraction methods, it would be most suitable to divide all of them into two main categories: solvent-based and solventless. Solvent-based methods use different types of solvents (no prizes for guessing) to dissolve trichomes "chemically", then the solvent is evaporated. Common advantages of these methods are high level of THC concentration in the final product, the drawback is that solvents may capture undesirable substances like chlorophyll and waxes and leave useful like terpenes. Besides, it's often impossible to completely remove the solvent from the final product.
What are the main production methods?
Butane/Propane
Perhaps Butane is the most popular hydrocarbon solvent, used in extraction at present. Plant material loads to a special tank with a valve at the top, liquid butane passed through it and flow out at the bottom. Products receiving by this method have the general title "butane hash oil" or BHO.
| Advantages | Downsides |
|
|
СO2
This is another commonly used method because it is safe, provides a clean end product, and gives a high degree of extraction.
To extract cannabinoids and other phytochemicals, carbon dioxide (CO2) is used under pressure. At certain temperatures and pressures, CO2 becomes to act as a solvent.
After extraction, CO2 is easily removed from the material, it is only enough to reduce the pressure and CO2 evaporates from the material without residue.
| Advantages | Downsides |
|
|
Ethanol
Plant material is placed in alcohol, which acts as a solvent. Ethanol is typically used. It is a powerful solvent and can extract the full range of cannabinoids and terpenes from the cannabis material.
| Advantages | Downsides |
|
|
Solventless methods used processes more related to physics, such as heating, refrigerating, pressure, etc. For example, Rosin is made by pressing plant material at high temperatures. Kief and hashes are made by sieving buds through the sifter in different ways.
What are the ways to consume extracts?
Extracts are fairly universal in smoking methods. In the absence of any special devices, they can be added to buds and smoked the way you usually use. Often they are used to bowl-topping when the extract is placed on the top of the bong bowl, filled with buds. Or added to buds, when rolling a blunt. These unsophisticated methods are well suited for extracts like kief, which close by its properties to buds. To a much lesser extent for THC-focused extracts with low terpenes content, like oils. The disadvantages of this way are that taste of extract gets lost against the backdrop of buds' taste, and the temperature of buds smoldering may be far from optimal to extract evaporation, so you lose the part of THC in the extract, that's combusted. It just sacrilege in relation to such jewels of extract world like live rosin or sauce.
So, to achieve the full potential of your extract I highly recommend using special devices: dab rig and vaporizer.
- A dab rig is basically alike usual water bong, but they're typically much smaller, and Instead of a bowl, it has a nail, also called banger. Nail is heated by a torch, then extract is placed inside and immediately evaporates from contact with a hot surface. Temperature is controlled by nail heat time.
- Vaporizers for extracts are another very effective way of consuming because, as a rule you can set temperature matching of your extract boiling point and pulling out the taste of your concentrate for a maximum.
There are many varieties of dub rigs and vaporizers. We have an extensive overview of them in our articles dedicated to all regards of using these fine devices.
What kinds of cannabis extracts exist?
And now, let's shortly go over the most common types of extracts. We collected the majority of products, which you can face in dispensaries of cannabis clubs.
Kief
Kief is a concentrated form of cannabis, created by separating the resin glands or trichomes from the cannabis flower, trichomes fall off easily when you grind or sieve it.
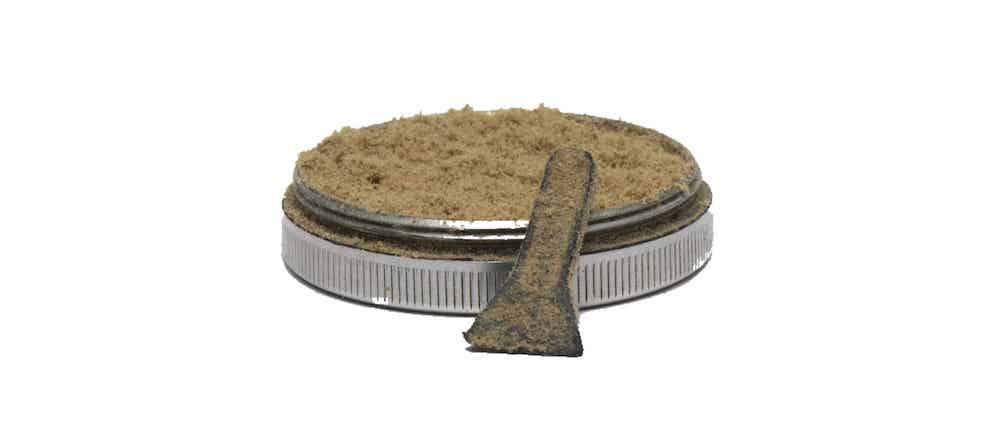

| Method of producing | Kief can be collected from grinders, different containers where cannabis is stored, or extracted using dry ice and other similar methods |
| Way of consuming | Probably the easiest way to enjoy kief - is just to smoke it. You can smoke kief like cannabis flowers, but it may be a little messy and tricky to deal with. Using a joint to smoke kief with buds is really convenient, to put some flowers in first, then add the kief and top to kief with some more flowers. This will put the kief in the center of the joint and help it burn more evenly when you smoke it |
| Content of THC | up to 65% |
Hashish
Hash is any concentrate from the pressed resin of the plant. Many hashes are kief, just subjected to high pressures.
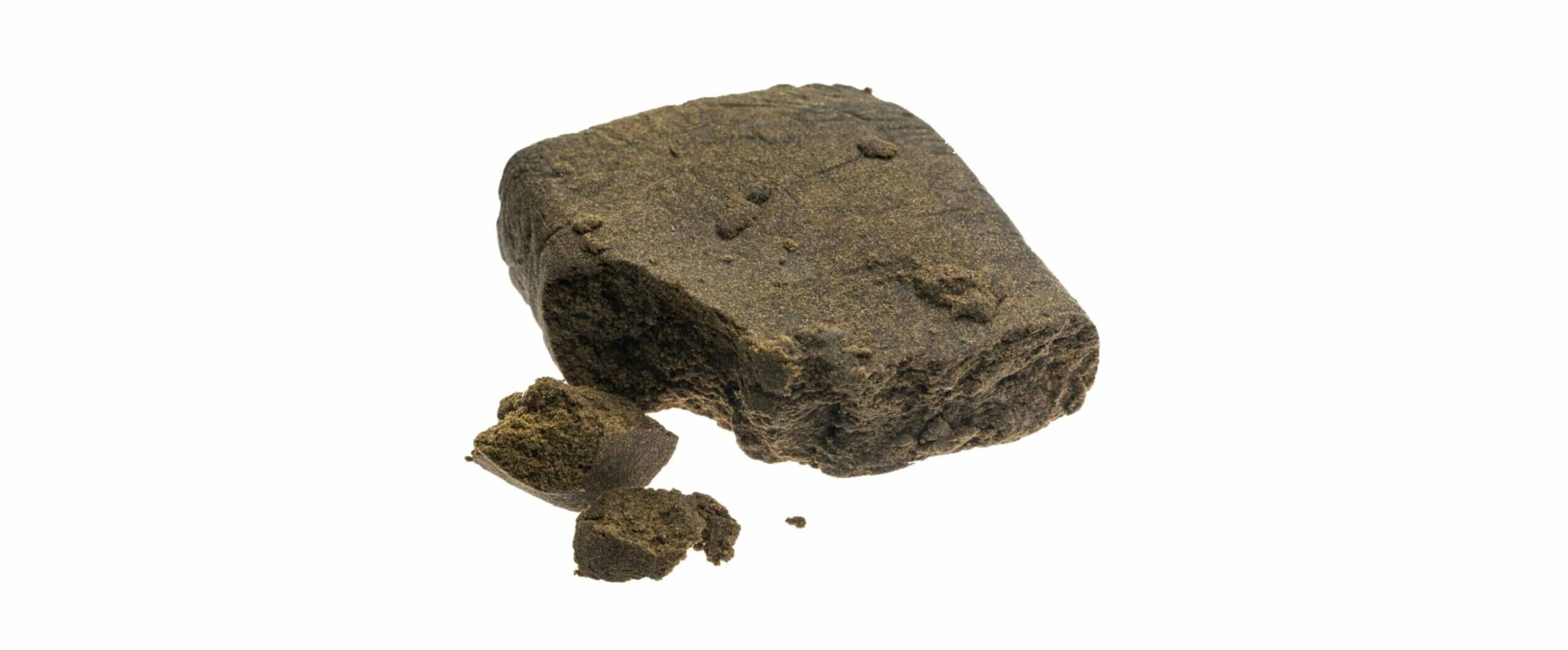

| Method of producing | There is a traditional way, which is still used in remote locations, in the historical motherland of hashish - India. Flowering plant press or rub between two hands and then forming the sticky resins into a small ball of hashish. Modern methods used the property of trichomes to become fragile under the low temperatures. When using the dry ice method, dry ice adding to plant material, then all mixed and sifted through a screen. In the bubble method, water in half with ice is poured into cannabis, all this is actively mixed, then filtered using a set of sieves. Then the resulting substance referred may be compressed into blocks of hashish |
| Way of consuming | Way of consuming: typically smoking in a pipe, bong, vaporizer, or joints, where it is normally mixed with cannabis or tobacco, because pure hashish will burn poorly alone |
| Content of THC | The range is very wide, from 4-18% in "street" hash made from wild growing cannabis, up to 65% in hashes made from high-grade marijuana |
Rosin
Melted cannabis resin in solid form. The all-natural extraction method fully transfers all properties of feedstock cannabis. The total absence of foreign substances in the extract.

| Method of producing | Made by pressing two hot plates with plant material in between, under very high pressure and the temperature is about 200 degrees. Heating makes trichomes to go from it's crystalline state to a more viscous, so it melts and flows. As feedstock also can be used bubble hash |
| Way of consuming | Dabbing, adding to any other way of smoking buds to increase potency |
| Content of THC | 60-80% |
Live rosin (frosin)
Likewise the rosin, but as feedstock fresh or freshly frozen buds used. Whereas full terpene profile of live uncured plant is transmitted.
| Method of producing | Duds frozen directly after harvest get out of the freezer immediately before the pressing, then, everything is happening like when regular rosin is made |
| Way of consuming | Dabbing |
| Content of THC | 50-70% |
Shatter
Hardest, glass-like type of BHO, very pure and potent but typically is not rich in terpenes.
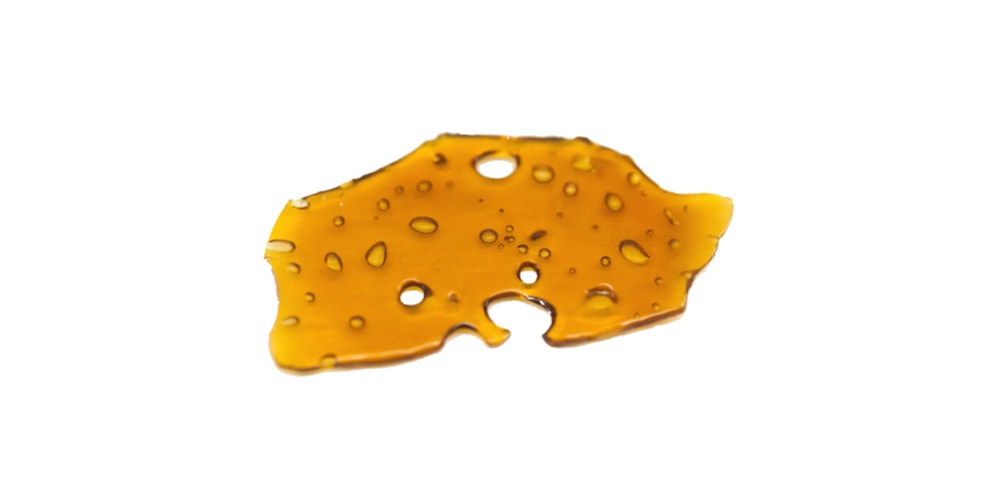

| Method of producing | Butane extraction |
| Way of consuming | Dabbing |
| Content of THC | 80% |
Pull and snap/Taffy
BHO or rosin extract, very similar to taffy by consistency. Convenient to operate with. Product received by rosin process called "taffy".
| Method of producing | Butane extraction, rosin process |
| Way of consuming | Dabbing, wrapping around joints, topping the bowl |
| Content of THC | 60-80% |
Budder
One of the best BHO extracts on the correlation of THC/terpenes, very potent and aromatic at the same time. It has a creamy texture similar to butter, easy to manipulate with.
| Method of producing | Butane extraction |
| Way of consuming | Dabbing, adding to joints or bongs bowl with regular buds |
| Content of THC | 80% |
Badder/Batter
Have a little more dry texture than a budder, but still malleable. A lot like cake frosting. Badder=batter, it's just a different way of saying.
| Method of producing | Butane extraction; less often - rosin process |
| Way of consuming | Dabbing |
| Content of THC | 60-80% |
Wax
One of the most common BHO on the market which has a consistency similar to... can you guess what?
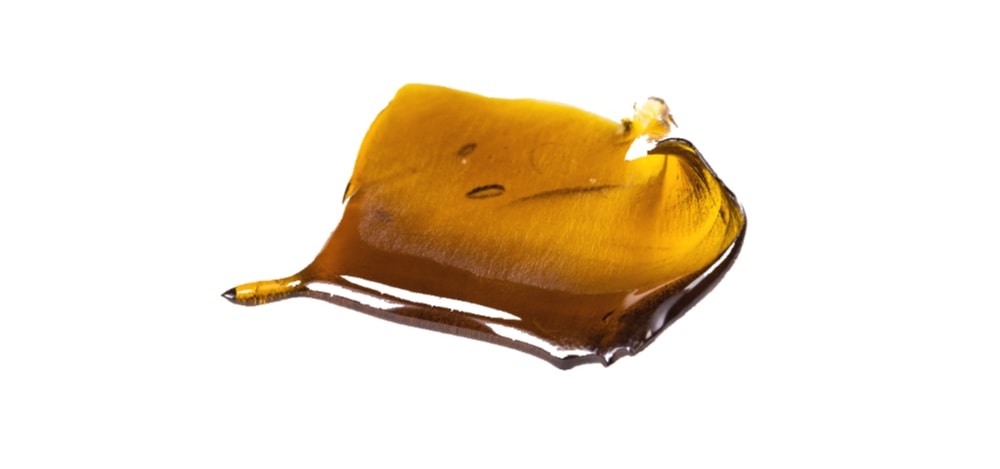

| Method of producing | butane extraction; rosin process |
| Way of consuming | dabbing, vaporizing |
| Content of THC | 60-80% |
Sugar/Sugar wax
BHO reminiscent soaked sugar. Sometimes results from an error of producing regular wax.
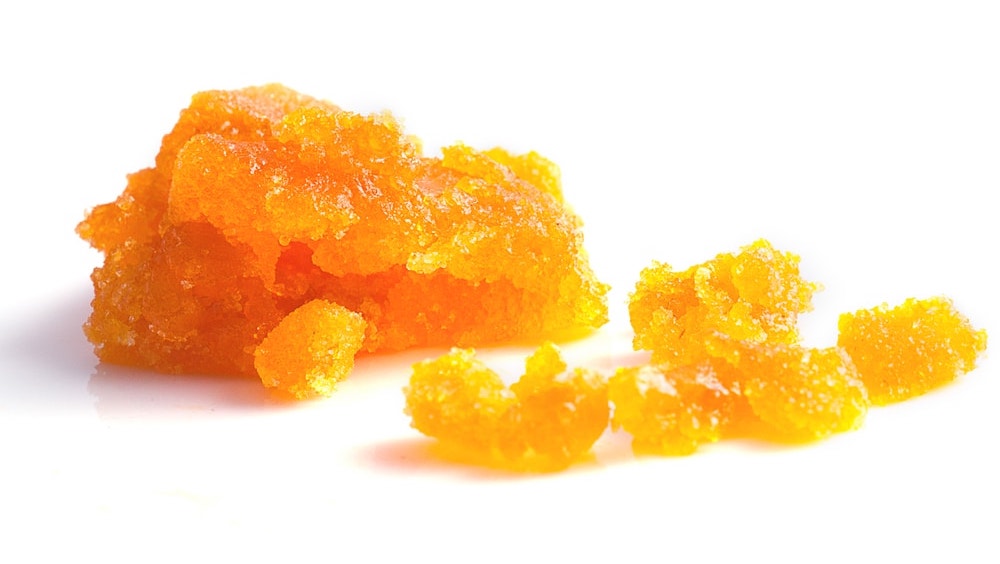

| Method of producing | Butane extraction; can be the result of transformation other types of BHO while storage |
| Way of consuming | Dabbing, vaporizing |
| Content of THC | 60-80% |
Crumble/Honeycomb wax
Another BHO extract whose name speaks for itself. Has a porous structure and tends to crumble when you operate it. Honeycomb wax has larger pores like a sponge.
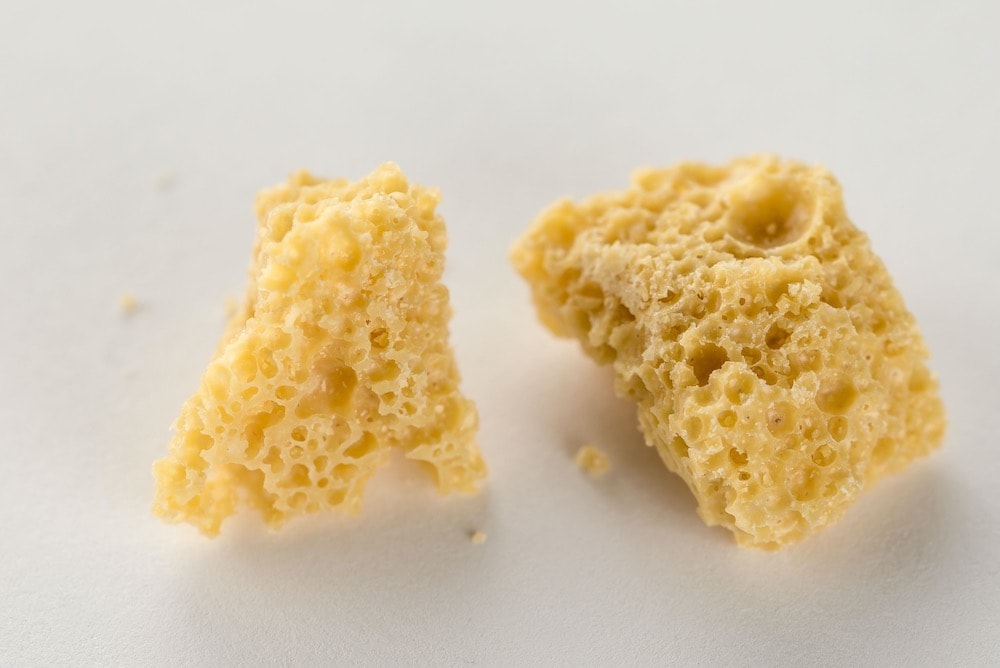

| Method of producing | Butane extraction |
| Way of consuming | Dabbing, vaporizing |
| Content of THC | 60-80% |
Live resin
BHO extract made from freshly frozen buds. Transmit the full terpene profile of the live plant.
| Method of producing | Butane extraction |
| Way of consuming | Dabbing |
| Content of THC | 60-80% |
Sauce, terp sauce, High Terpene Full Spectrum Extract (HTFSE)
Subspecies of extracts with a focus on terpenes, which can represent more than 50%. Most often look like liquid honey or consists of two fractions: amber-colored liquid and transparent crystals in it.
| Method of producing | Butane extraction of dried or freshly frozen plant material |
| Way of consuming | Dabbing, vaporizing |
| Content of THC | near 50% |
Sap
Viscous, sticky extract, resembling a tree sap.
| Method of producing | Butane extraction, rosin process |
| Way of consuming | Dabbing, vaping, adding to joints or bongs bowl with regular buds |
| Content of THC | 60-80% |
Oil/CO2 Oil
Liquid extract, translucent with different shades of yellow, usually used in vape cartridges. Has a high level of purity as a rule.
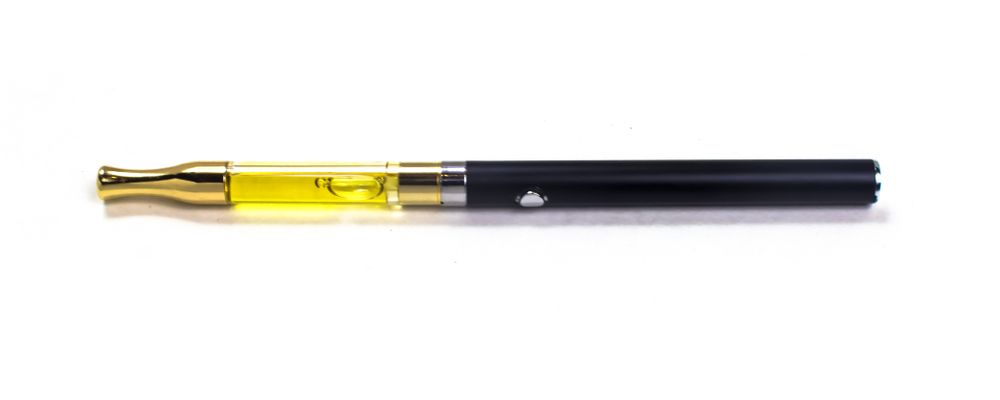

| Method of producing | Butane extraction, CO2 extraction |
| Way of consuming | Vaping, adding to joints or bongs bowl with regular buds |
| Content of THC | 80-95% |
Distillate
Almost pure cannabinoid, THC or CBD. Free of any substances like terpenes, waxes, chlorophyll, etc. Quality samples usually transparent and have no smell.
| Method of producing | Extraction with hydrocarbon or CO2 solvent with subsequent distillation in a fractionating column |
| Way of consuming | Vaping, dubs, orally (under the tongue) |
| Content of THC | 90-99% |
Crystalline
Shiny crystals of chemically pure cannabinoid THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid), CBD, or CBDA (cannabidiolic acid).
| Method of producing | Extraction with hydrocarbon or CO2 solvent with subsequent purification |
| Way of consuming | For medical purposes orally, adding to other concentrates for increasing of potency |
| Content of THC | 99.9% |
Moon rocks/Caviar
The "delicacy" of the cannabis world, moon rocks are buds covered with hash oil then sprinkled of kief. Caviar is the same thing, but sometimes without kief. Therefore any moon rock is caviar, but not all caviar is a moon rock.
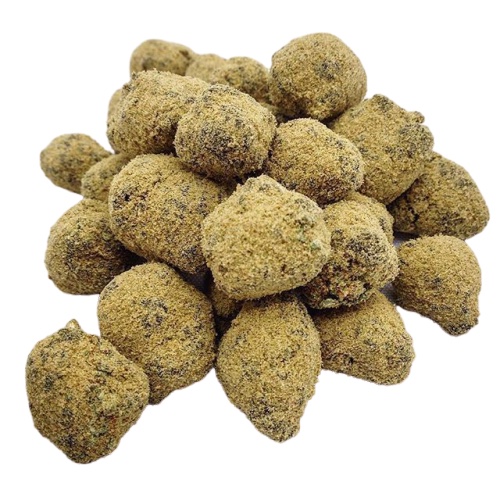

| Method of producing | Buds dipping in hash oil, then in kief |
| Way of consuming | Bong |
| Content of THC | over 50% |
Rick Simpson Oil (RSO)
Rick Simpson Oil (RSO) is a type of alcohol-derived extract created by marijuana activist Rick Simpson, which used it to heal cancer. It is pretty easy to produce, so it can be done even at home.
| Method of producing | Ethanol extraction |
| Way of consuming | Orally as sublingual drops or in capsules, rub in skin |
| Content of THC | 20% |
Conclusion
I would like to underline - cannabis concentrates are very potential and require to show restraint when using. If you will be consistent and will use your common sense when interacting with them you can enhance your cannabis experience. The average weed you smoke is in the 15% to 25% THC range, mostly extracts range in the 60%-80% of THC. Therefore, make sure you know what you're doing before you inhale. So, be sensible, and have a good time!




